

mean value, standard deviation, count, minimum and maximum values. See note below.ĭynamic Surface: During data acquisition if you add new soundings to grid cells that have previously been filled, the new data OVERWRITES the existing and new attributes are computed for the new data, i.e. Sounding Grid: During data acquisition if you add new soundings to grid cells that have previously been filled, the new data is MERGED with the existing and new attributes are computed, i.e.
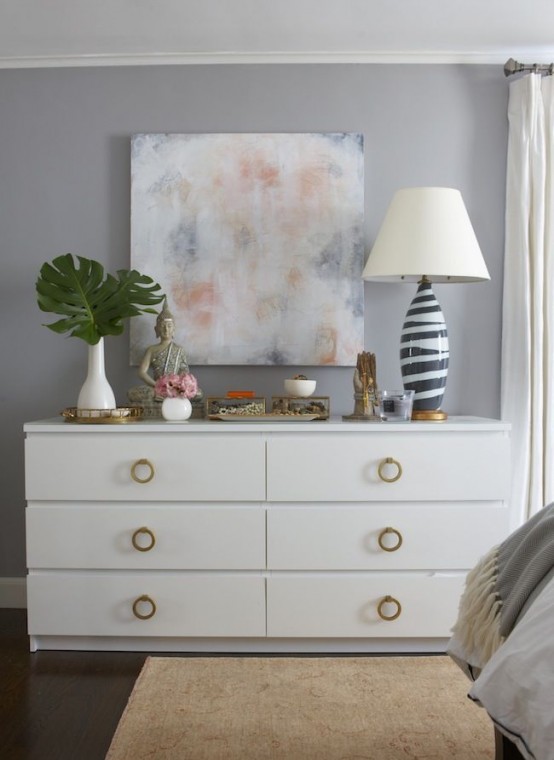

Sounding Grid versus Dynamic Surface (acquisition mode)Įach type can be created both in the Controller and in the Processing Manager.
Processing Manager - File - New - Sounding Grid: This option uses the previous sounding grid program. At startup only one layer is predefined. It uses the newer Creating a New Sounding Grid program. At startup a number of predefined layers are available for activation. Controller - Settings - Session Setup - Storage - Sounding Grid: This is the best option for dredging. There are two primary places for creating a new sounding grid: \Program Files (x86)\QPS\QINSy 8.1\SoundingGridUtility.exe. The former application is still available and is used by default when creating a new grid in the Processing Manager, and when using the stand-alone program, i.e. Online the following dredging related data can be stored to the sounding grid: Add layers to an existing sounding grid file. Change the grid settings of a new sounding grid file. The new application was included in the Autumn 2015 release of QINSy and is used by default when creating a sounding grid from the Session Setup Storage option in the Controller. This mechanism is used when scaling the navigation display, in generating contours and in data export.Ĭreating a New Sounding Grid - Program Functionality So for example, if the minimum cell size is chosen to be 1m x 1m, the following grid levels are generated: 2x2, 4x4, 8x8, 16x16 and 64圆4 as an overview level. Based on the user defined minimum cell size, five additional grids are automatically generated on-the-fly. design layer, in-survey layer, mixture density, mixture velocity, etc. User defined layers employed to store and visualize data of different kinds, e.g. The grid is generated on-the-fly and has no boundary. Calculate volumes, show statistics, create contours and spot soundings for ENC's, DXF’s and PRO’s. real-time dredged depth versus design depth. Compute and display surface differences, e.g. 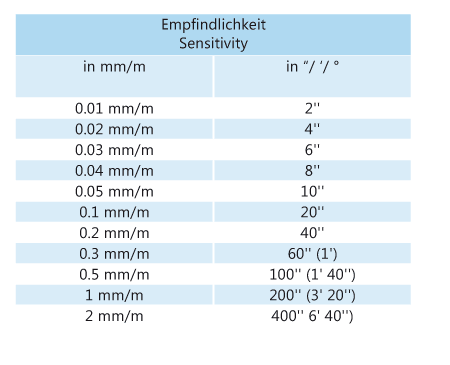
Simultaneously store and visualize data of different kinds, including data attributes such as 95% confidence level, min/max values, etc.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
